Dear Editor,
The Renbök phenomenon refers to an area of non-involvement in an otherwise generalised skin disease. Here, we describe a case with coexisting alopecia areata (AA) and vitiligo with retained hair growth localised to the vitiligo lesion. The development of alopecia areata-sparing vitiligo has not been reported previously.
A 50-year-old woman presented with a depigmented patch on the occipital scalp 10 months ago. During the subsequent months, scalp hair loss was observed. She was otherwise healthy, did not take any medications, and had no family history of AA or vitiligo. Remarkably, the symptoms of AA were spared in the white patch, which exhibited pigmented terminal hairs [Figure 1a]. Physical examination revealed extensive hair loss on the occipital skin, including the depigmented patch, but most hairs in the white patch were retained. Dermoscopy revealed black dots, broken hairs, and perifollicular pigmentation [Figure 1b]. We diagnosed this case as vitiligo, accompanied by AA.
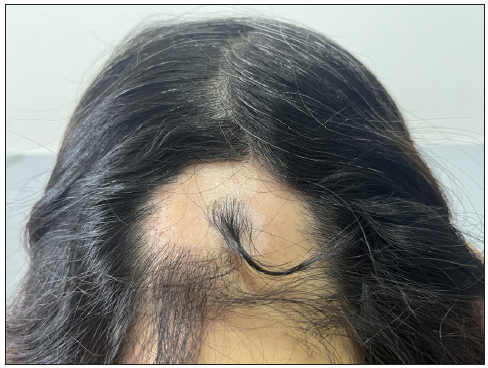
Export to PPT
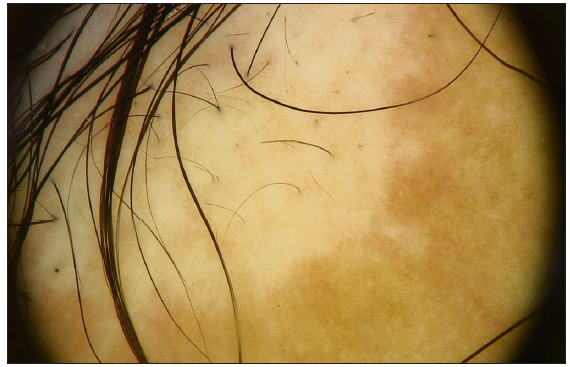
Export to PPT
In 1991, Happle et al. first described the Renbök phenomenon in a patient with psoriasis and AA with non-colocalisation.1 In addition to AA, the Renbök phenomenon can spare areas of naevus flammeus, Becker’s naevus, vascular naevus, melanocytic naevus, and scalp sarcoidosis.2 There have also been reports of drug-related eruptions, Stevens‒Johnson syndrome, and contact immunotherapy-induced Renbök phenomenon.3 The duelling cytokines theory is one potential explanation for the complex development of this phenomenon; in this theory, the Renbök phenomenon occurs after inflammatory amplification via the activation of a subset of T helper (Th) cells (Th1, Th2, and Th17). Positive feedback is sustained through the release of related cytokines from Th cells.2
Previous studies of the underlying pathogenesis of both AA and vitiligo have focused on the interferon gamma-driven autoimmune response.4 These specific immune responses target the anagen-stage AA hair follicle bulbs as well as melanocytes in the basal layer of the epidermis in vitiligo, both of which may be caused by abnormal melanocyte autoantigen exposure, the “original perpetrator”.5,6
AA is known to influence pigmented (black or dark brown) hairs and potentially spare white hairs; therefore, we speculated that pigmented hairs in patients are vulnerable to autoantibodies, which preferentially target the melanocytes of the hair follicle. The immune privilege of hair follicles is thought to protect against AA and may be responsible for protecting hair from depigmentation in vitiligo.6 In this case, the vitiligo patch subsequently developed AA, and the existing vitiligo lesion counteracted AA areata progression and retained the hair. We hypothesised that the collapse of immune privilege in hair follicles plays an important role in the interaction between the different autoimmune patterns of the two diseases.
The unique hair residues in vitiligo lesions suggested that the immune pattern of vitiligo could affect the immune privilege of hair follicles under autoimmune attack. We believe that this phenomenon supports a new type of Renbök phenomenon in AA, which helps to elucidate the underlying mechanisms and potential treatment strategies for AA.
Comments (0)