In 1883, German scientist Ludwig Knorr made the pyrazole nucleus discovery. The nucleus and chromones were first discovered by Walther Flemming in 1882. The pyrazole nucleus has a five-membered heterocycle with two nitrogen atoms next to one another. Neighboring nitrogen atoms can be found in heterocylic compounds.1,2 Chromones are benzoannelated -pyrone-ringed heterocyclic compounds containing a single oxygen ring. 4H-chromen-4-one, also referred to as 4H-1-benzopyran-4-one, is the parent substance. Chromones and pyrazole include considerable amounts of heterocyclic nuclei because of the wide range of therapeutic applications for these elements. In Figure 1 below, chromones and pyrazole are shown. Today, chromones and pyrazole exhibit a variety of pharmacological properties. Chromones have a molecular weight of 146.14 g/mol and the chemical formula C9H6O2. Pyrazole has the chemical formula C3H4N2.³ and a molecular weight of 68.07 g/mol. particularly, the molecule with the chromones and pyrazole rings coupled to electron-withdrawing and electron-donating groups shown stronger inhibitory potential against bacterial and fungal strains than conventional medicine. Chromones and pyrazole both possess broad-spectrum anti-bacterial, anti-inflammatory, analgesic, anti-tubercular, antihypertensive, anticonvulsant, and antiviral activity, according to a conclusion drawn after reading multiple study and review articles.4Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, and other parasitic or pathogenic micro-organisms have a marginally detrimental effect on human health. These microbial growths cause the host tissue to be destroyed and can cause fatal infections. Food poisoning, fever, and diarrhoea are symptoms of the bacterial parasites Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli. Millions of people in poorer nations are also impacted. More than 80 million individuals worldwide are afflicted, and up to 1,30,000 people die from these illnesses each year. To treat these infections, a variety of medications, including Gentamycin, Amoxicillin, Norfloxacin, and Ciprofloxacin, are available on the market.1,6 They have substantial negative effects while being the most often recommended drugs for this bacterial disease. Based on these contributions, we will continue our drug research programme in order to produce interest in the synthesis of a new series of chromones and pyrazole to create more effective and toxic-free antimicrobial agents. This research will focus on the creation of new, safer, and more biologically active derivatives. Diverse biological processes have been associated with heterocyclic compounds comprising nitrogen and oxygen atoms. Chromones and pyrazole derivatives have a considerable impact on the medical industry thanks to their wide range of pharmacological actions.1–11 such as their anti-bacterial, anti-viral, anti-diabetic, and anti-cancer activity. The information that implies that the substitution at the 2 and 5 positions considerably alters the pharmacological properties of these compounds has piqued the interest of numerous research teams in chromones and pyrazole. Particularly, compounds having both electron-withdrawing groups, such as chloro and fluoro connected with the Chromones ring and Pyrazole, showed more inhibitory ability against bacterial and fungal strains than conventional medicine. As a result, various research groups have worked to find novel antimicrobial medications and the WHO and new scientists around the world have made significant efforts to treat these illnesses. However, pharmacologically, chromones and pyrazole, together with their derivatives, comprise the most significant class of organic heterocyclic compounds having anti-microbial capabilities, such as anti-bacterial, anti-fungal, herbicidal, and anti-viral activity.
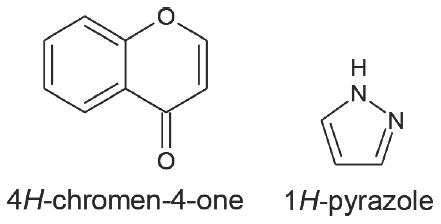
Figure 1:
Chromones and Pyrazole heterocyclic nucleus
Comments (0)